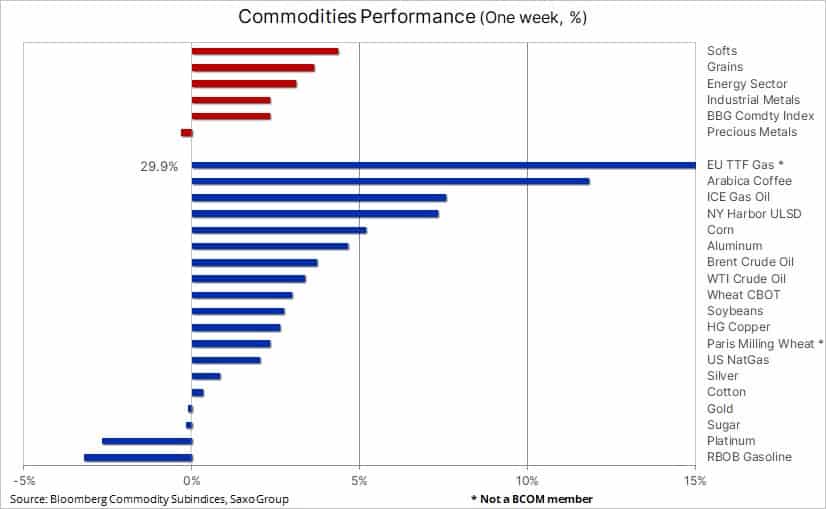
The commodity sector continues to recover as the Bloomberg Commodity Index claws back more than half of what it lost during the June to July 20% correction. Gains were seen across most sectors, led by agriculture as weather woes lifted the cost of coffee and the three major crops – especially corn. Industrial metals received a boost from China’s continued efforts to support its weakening economy by announcing more stimulus policies that would pump billions into infrastructure projects. The energy sector was supported by surging gas prices driving up demand for diesel and Saudi Arabia flagging the risk that OPEC+ may cut production to stabilise volatile markets.
In financial markets, the dollar reached a fresh 20-year high against the euro as Europe’s energy crisis continued to pressure the economic outlook for the region. US stocks tumbled and bond yields rose. Inflation-fighting measures, such as hiking interest rates and removing stimulus into a post-pandemic economic slowdown, was the main driver behind the recent correction in commodities.
Overall, however, we maintain the view that commodities can weather headwinds from an economic slowdown with supply of key commodities being equally challenged. In the long term, support for commodities will be driven by underinvestment, urbanisation, the green transformation and deglobalisation. In the short term, prices are likely to be supported by the unfolding energy crisis in Europe, Russia-sanctions related supply disruptions, adverse weather raising fresh concerns about food supplies, and China’s efforts to support its economy.
Crude oil sellers having second thoughts
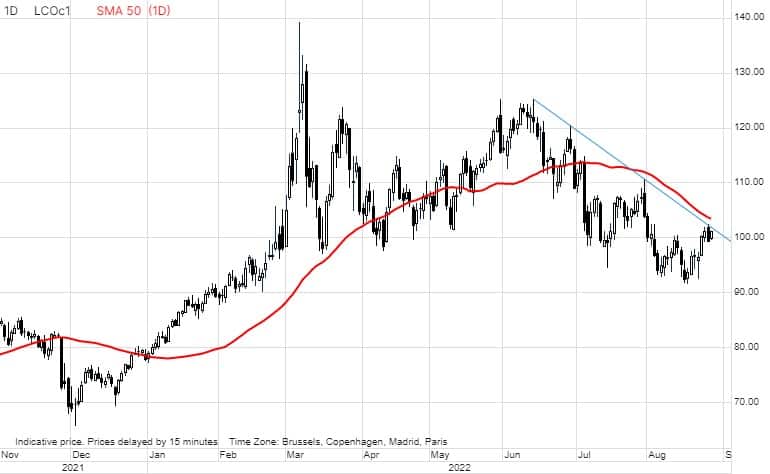
While the macro-economic outlook remains challenging due to the lower growth outlook and recent dollar strength, crude oil and the product markets have nevertheless managed a strong rebound this past week. The energy crisis in Europe continues to strengthen, with gas and power prices surging to levels that measured in dollars per barrel of crude oil equivalent equates to $530 and $1,400 per barrel, respectively. The latest surge was driven by recent low-water level disruptions on the river Rhine and Gazprom announcing a three-day closure of the Nord Stream 1 pipeline due to maintenance, starting on August 31.
Should Gazprom (President Putin) decide to weaponize supplies further and keep the pipeline shut after maintenance ends, the risk of further spikes remains – thereby extending the already wide price gap between gas and crude oil. A development that will further support an already very visible increase in demand for fuel-based product, especially diesel and later on this autumn also heating oil, at the expense of gas. This gas-to-fuel switch has supported the recent recovery with the US last week shipping a record amount of diesel to energy-starved customers looking for alternatives to Russian supplies.
However, the trigger which eventually sent crude oil higher this week were comments from the Saudi Energy Minister and other OPEC members. These comments flagged possible cuts to production following a recent and growing disconnect between falling futures markets and a physical market that has yet to show weakness. A discrepancy we have noticed as well in recent weeks with crude oil futures being sold as a hedge against an economic slowdown with little focus on the physical market and its current price supportive supply and demand fundamentals.
Having found support after retracing 61.8% of the December to March 111% surge, the Brent crude oil futures contract has now returned to $100 per barrel with trendline resistance, currently $102.25 preventing a further upside push. A continued recovery at this point may force money managers to reassess their exposure in Brent and WTI with a potential short-squeeze brewing. During a three-week period to August 16, speculative traders reduced their net long to 278k lots, the lowest since April 2020.
Rising grain prices and strong dollar re-ignite food supply worries.
U.S. corn reached a two-month high and, together with more muted gains across the other major US traded crop futures, the Bloomberg Commodity Grain Index has now risen by 12% following the May to July correction which at least temporarily helped reduced worries about a global food crisis. However, with bad weather continuing to impact production and with Ukraine exports still well below previous years, the mentioned worries have started to re-emerge – not least considering the recent run up in the dollar which has only made matters worse for buyers of grains in local currencies.
The latest run up in US corn has been supported by concerns that hot and dry weather in the Midwest during the final crop development period may limit the production outcome. The US is the biggest producer and exporter of corn – which is used in everything from animal feed to biofuels and sweeteners – and a poor US harvest will likely rekindle recent worries about food security that was driven by war, drought and the overall impact of climate change.
In addition to the above and the mentioned slow pace of shipments from Ukraine, we are currently seeing drought in China threatening the local harvest which could lead to higher imports. Dryness within the European Union this summer has continued to drive production forecast lower.
Coffee prices surge on Brazil and Vietnam supply worries
Both Arabica and Robusta coffee futures returned to strength, both rallying strongly on signs of a deteriorating supply outlook. Stockpiles in Vietnam – the world’s top supplier of the Robusta variety – are expected to halve by the end of September from a year earlier while stocks of the Arabica bean monitored by the ICE exchange has slumped to a 23-year low. Freak weather in South America during the past year has decimated the production outlook for Brazil, Colombia and Central America, while recent dryness and a continued surge in the cost of fertilizer have already started to raise concerns about next year’s crop. The Arabica futures contract paused after reaching the June high at $2.42 per pound, but the risk remains that it may push towards the 11-year high at $2.605 reached in February
Industrial metals find support in China
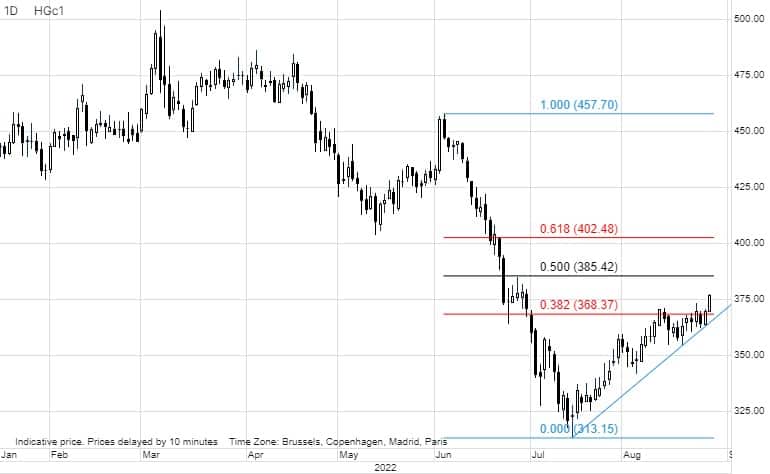
Industrial metals, led by steel, aluminum and zinc responded positively to news that the Chinese government has stepped up its efforts to support an economy damaged by repeated Covid lockdowns and a property market slump. China’s State Council announced a 1 trillion yuan ($146 billion) stimulus package with 300 billion going towards infrastructure projects, thereby doubling the amount the government has pledged towards project that will boost demand for industrial metals.
Following a period of range trading between $3.55 to $3.73, High Grade Copper broke higher on Friday and may now target $3.85/lb next, but it will likely require a rally above $4/lb before speculators, having traded the metal with a short bias since April, start to reverse back to a net long. The primary focus remains on China and whether the mentioned stimulus measures will be strong enough to shore up enough support for the upside push to continue.
Gold trades steady despite fresh dollar and yield strength
Gold managed a small bounce but overall, it continued its recent struggle amid headwinds from a stronger dollar and rising bond yields. Not least ahead of Friday’s Jackson Hole speech from Fed chair Powell with gold traders worried that a hawkish statement would provide additional strength to the dollar and yields, thereby further delaying gold’s return to strength by potentially sending it below support at $1729.
In a year where inflation has been surging higher, some investors may feel hard done by gold’s negative year-to-date performance in dollars but taking into account it had to deal with the biggest jump in real yields in more than 25 years and the dollar rising 10% against a broad basket of major currencies, its performance, especially for non-dollar investors remains acceptable.
We maintain the view that the market is overly optimistic with the assumption that central banks can successfully bring inflation down to the levels currently being projected. Such a scenario would create a challenging outlook for interest rate and growth sensitive stocks, thereby raising the need for tangible assets such as gold and commodities in general to weather a period of low growth and high inflation.
Natural gas, now the biggest component in the Bloomberg Commodity index
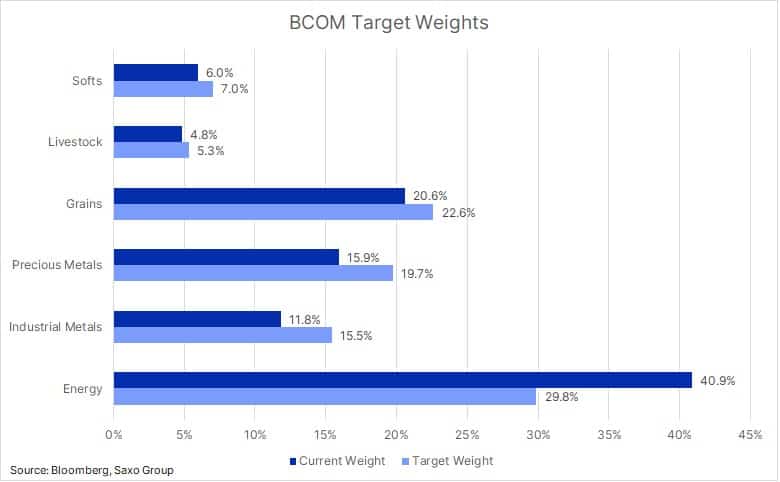
The BCOM index together with the S&P GSCI and DBIQ Optimum Yield Diversified Commodity Index belongs to the heavy weights within the global investment industry for commodities. It tracks the performance of 23 major commodity futures targeting a one-third exposure in the main sectors of energy, metals and agriculture. The target weights are set once a year every January and if prices shift significantly during the year, a reweighting will not occur until the following January.
However, an astonishing 160% year-to-date surge in US natural gas futures has more than doubled its weight to 17.2% from 8%, and made it the biggest component in the BCOM index for the first time ever – more than double that of WTI and Brent combined. From a sector perspective, it has helped lift the total energy exposure by 9.2% to 40.9%. All other sectors and sub-sectors have seen reductions with the biggest impacting industrial and precious metals by a combined reduction of 7.5%. These moves away from target weights will not be adjusted until next January. At which point, we may see some major activity as the rebalancing process would see selling of gainers, especially natural gas while the biggest losers will be bought.
Ole S. Hansen is the Head of Commodity at Saxo Bank.
The opinions expressed are those of the author and may not reflect the editorial policy or an official position held by TRENDS.