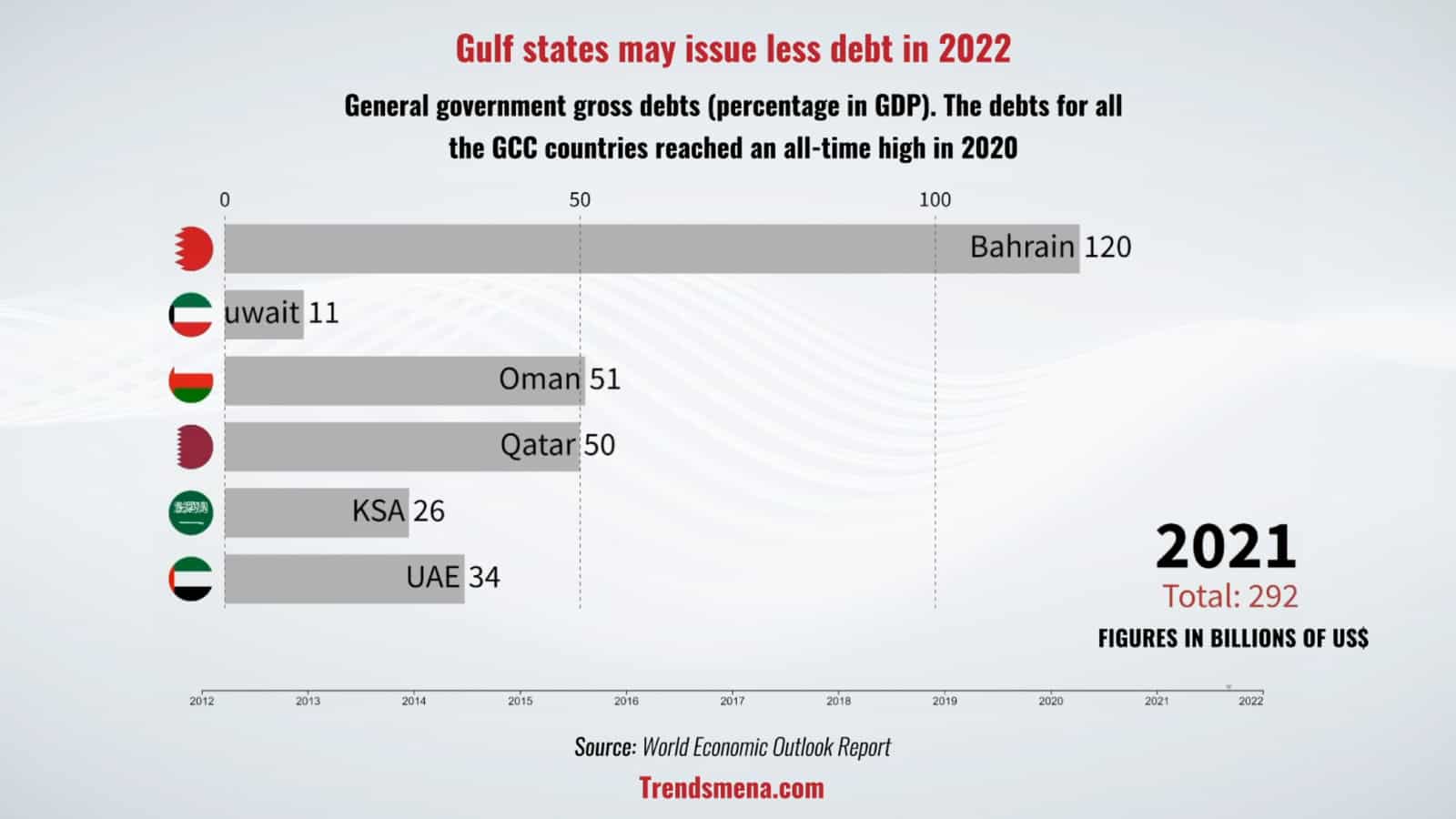
The GCC countries are expected to issue lesser debt in 2022 than 2021, after having issued a record amount of debt in 2020.
The reason appears to be the better fiscal positions thanks to high oil prices and the recovery of economy from the Covid pandemic’s effects.
In 2020, international debt issued by Saudi Arabia, the UAE, Qatar, Bahrain and Oman was $42.1 billion, up 25 percent from $33.5 billion in 2019, driven by higher deficit financing needs resulting from lower oil prices and the impact of Covid-19.
Debt-to-GDP ratio is a measure of a country’s ability to pay back public debt: a high ratio may be an indication that a country could find it harder to pay off its external debts.
Analysts last year were especially concerned about Bahrain and Oman whose government debt ratios had risen sharply in recent years.
TRENDS takes a look at the general government gross debt (percentage in GDP) of GCC countries in recent years: