DUBAI, UAE — In 2023, the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) region witnessed significant advancements in its space sector, with various initiatives and projects marking a new era of space exploration and technology development. This year’s developments underscore the GCC’s increasing role in the global space race, driven by technological advancements, strategic partnerships, and substantial investments.
Saudi Arabia: A Regional Leader in Space
In 2023, Saudi Arabia’s space sector made significant strides, particularly with the transformation of the Saudi Space Commission into a full-fledged government agency, now known as the Saudi Space Agency (SSA). This development reflects the Kingdom’s deepening commitment to space exploration and technology as part of its Vision 2030 initiative, aimed at economic diversification and technological advancement.
A highlight of Saudi Arabia’s space endeavors in 2023 was the launch of its first mission to the International Space Station (ISS), which included two Saudi astronauts, one of whom was the first female astronaut from the Arab world. This mission, sponsored by the Saudi government, was led by the US-based space infrastructure developer Axiom Space. The SSA’s focus areas, outlined in the national space strategy released in 2023, include tourism, photography, satellite communications, and exploration. This strategy aligns with the nation’s broader goals of enhancing technical capabilities and expertise in aerospace engineering, satellite manufacturing, and advanced research and development.

Saudi Arabia’s increased involvement in space activities and its expanding partnerships, including discussions on enhancing cooperation with the World Bank, demonstrate the Kingdom’s aspirations to become a major player in the global space sector. These efforts are part of a broader strategy under Saudi Vision 2030 to transform the Kingdom’s economy and establish itself as a leader in various high-tech industries, including space.
UAE: Pioneering the Arab World’s Space Ambitions
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) has continued to establish itself as a leader in space exploration in the Arab world, particularly through significant developments in 2023. The UAE’s space program, initiated in 2014, has achieved numerous milestones, including the successful Hope Probe mission to Mars in 2021, positioning the UAE as the first Arab state and the fifth globally to achieve this feat.
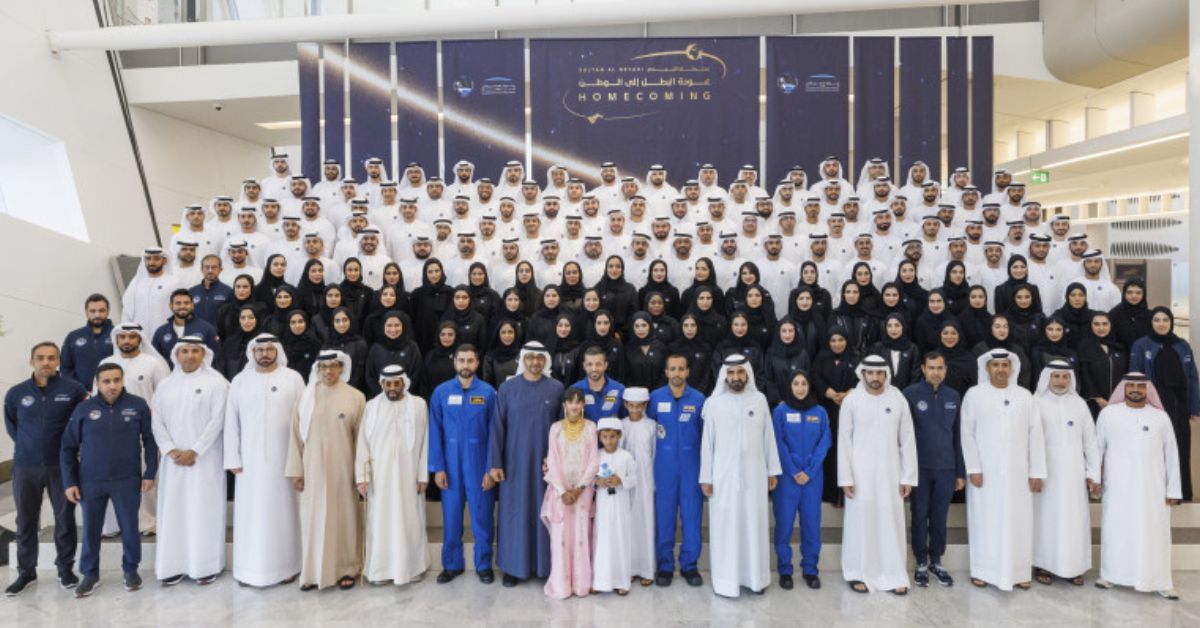
In 2023, the UAE’s space exploration efforts reached new heights, with several ambitious missions and initiatives underway. One of the most notable achievements was the mission involving Emirati astronaut Sultan Al Neyadi, who embarked on a six-month trip to the International Space Station (ISS). This mission marked a significant moment in the Arab world’s space exploration history, with Al Neyadi becoming the first Arab astronaut to undertake a long-duration space mission. The mission’s primary focus was on conducting in-depth and advanced scientific experiments, contributing to the global understanding of long-duration spaceflight’s impact on astronauts and aiding in preparations for future crewed missions to Mars.
Another significant development in 2023 was the UAE’s lunar mission, which aimed to land the Rashid rover on the Moon. This rover, developed by a team of Emirati engineers at the Mohammed bin Rashid Space Centre (MBRSC), was scheduled to launch in November from Cape Canaveral, Florida, aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. The rover’s journey to the Moon was expected to take approximately three months, with the landing attempt scheduled for early 2023. If successful, the UAE would become the first Arab country to reach the Moon.

Additionally, the UAE planned to launch the MBZ-Sat, the region’s most advanced imaging satellite, by the end of 2023. This 800-kilogram satellite, designed and built entirely by Emirati engineers, was expected to be carried into orbit on a SpaceX ride-sharing mission. The satellite’s development involved collaboration with five private companies in the UAE, emphasizing the country’s efforts to support the local space industry.
The Payload Hosting Initiative (PHI) satellite, developed under a United Nations platform, was another project scheduled for launch in 2023. This demo satellite, featuring unique payloads such as a water-fueled propulsion subsystem and an Internet of Things communication system, aimed to offer new opportunities for startups and developing space nations.
The UAE Space Agency’s strategic approach to fostering the space sector’s growth has included collaborations with Masdar City in Abu Dhabi to establish the first space economic zone. Additional zones were planned for Dubai and Sharjah to provide a conducive environment for international companies to establish operations in the Emirates. This initiative was part of the UAE’s broader efforts to develop a sustainable and self-reliant space program, focusing on building local expertise and capacity.
The Emirates Mars Mission, which successfully sent the Hope spacecraft to Mars, laid the foundation for the UAE’s private space sector development. The mission’s impact extended beyond scientific achievements, driving public awareness and interest in space, science, and technology, and stimulating the creation of space-related startups.
These developments demonstrate the UAE’s ambitious vision to become a leading space power in the region and globally. The nation’s investment in space exploration and technology, along with its emphasis on collaboration and innovation, positions the UAE at the forefront of the Arab world’s space endeavors.
Bahrain’s Growing Space Aspirations
In 2023, Bahrain, as part of its National Space Science Agency (NSSA), has made significant advancements in its space program, aligning its space capabilities with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The Kingdom has embarked on ambitious projects, demonstrating its growing aspirations in the space sector and its commitment to leveraging space technologies for sustainable development.
Launch of the First Fully Bahraini-Built Satellite: A landmark achievement for Bahrain in 2023 was the announcement of its first entirely locally-built satellite, set to be launched by December 2023. This project, led by Bahraini youth skilled in space science and technology, marks a new milestone in the Kingdom’s space sector. It reflects the national spirit, determination, and resolve of Bahraini youth to enhance the country’s status in the field of space science. Sheikh Nasser bin Hamad Al-Khalifa, a key figure in this initiative, has expressed appreciation for the Bahrain Space Team’s scientific contributions and the NSSA’s management for their tremendous effort in positioning Bahrain among the leading countries in the field of space. This project is part of NSSA’s strategy that begins with the launch of this satellite and extends through 2028, highlighting a long-term commitment to space exploration and technology development.
Collaboration with Regional and International Partners: Bahrain’s space program is characterized by its collaboration with regional partners, particularly the UAE Space Agency, as well as international partnerships. One of the notable collaborations is with the UK, as part of a ‘space bridge’ program. This program, involving cutting-edge companies from the UAE, Bahrain, and the UK, is focused on developing advanced space technologies to address challenges such as natural disasters and reducing greenhouse emissions in the Gulf region. The initiative, supported by the UK Space Agency’s International Bilateral Fund, aims to boost international partnerships and facilitate collaboration on space projects. This collaboration offers opportunities for UK space companies to enter and service the GCC region, creating strong international trade and investment ties. It reflects Bahrain’s proactive approach in embracing international cooperation to enhance its space capabilities.
Focus on Sustainable Development through Space Technologies: Bahrain’s space endeavors are closely aligned with sustainable development goals, reflecting a strategic approach to using space technologies for broader societal benefits. This alignment showcases Bahrain’s commitment to leveraging space exploration not just for scientific discovery but also for addressing global challenges such as climate change, resource management, and disaster response. The Kingdom’s focus on sustainable development through space technologies is a testament to its forward-thinking approach in the space sector.
To sum it up, Bahrain’s space program in 2023 has been marked by significant milestones, including the development of its first fully Bahraini-built satellite and strategic collaborations with regional and international partners. These developments signify Bahrain’s growing presence in the space sector and its commitment to using space technology for sustainable development and international cooperation.
Kuwait’s Private Sector-Led Space Initiative
Kuwait’s foray into space in 2023 marked a significant milestone in the country’s space industry, led primarily by private sector initiatives rather than government-led projects. This approach represents a shift towards a more grassroots development in the space sector within the Gulf region, emphasizing the role of private enterprises in driving innovation and progress.
A key player in Kuwait’s private sector-led space initiative is Orbital Space, which became the first company in the region to specialize in CubeSat technology and establish a private CubeSat ground station in the Middle East. Orbital Space’s efforts reflect the burgeoning interest and capability in the space sector in Kuwait, highlighting the country’s potential to contribute significantly to the global space industry.
In a landmark achievement, “Kuwait Sat-1” was successfully launched into space, marking Kuwait’s debut in satellite technology. This achievement was the culmination of three years of diligent work, aiming to bring Kuwait’s space ambitions to fruition. The satellite was launched onboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Cape Canaveral in Florida, in a project undertaken by Kuwait University and funded by the Kuwait Foundation for the Advancement of Sciences. The launch of Kuwait Sat-1 is seen as a foundational step in setting up Kuwait’s space industry and aligning with the country’s 2035 vision to establish national capabilities in scientific fields, including space technology.

The project was not only a technical achievement but also a collaborative effort involving a large team of Kuwaiti students and professionals. It reflects Kuwait’s commitment to developing national expertise in space technology and its determination to participate actively in the space sector. The satellite’s launch was monitored through a ground reception station, which will receive information from imagery collected by the satellite, located at the Sabah Al-Salem Science City in Kuwait University’s campus. The project’s success is attributed to the collective efforts of the Kuwaiti team, which managed to overcome numerous challenges and obstacles to achieve this historic milestone.
This development in Kuwait’s space sector is indicative of the broader trend in the GCC region, where countries are increasingly recognizing the importance of space technology and exploration. Through such initiatives, Kuwait is positioning itself as a key player in the space sector, not only in the GCC but also on the global stage.
Oman’s Space Development Initiatives
Oman has taken bold steps in its space development program, with several key projects and strategies aimed at enhancing its space capabilities:
Spaceport Development: Oman announced plans to construct the Middle East’s first space rocket launch center, the Etlaq Space Launch Complex, in the port town of Duqm. This project, overseen by the Sultanate’s National Aerospace Services Company (Nascom), is designed to promote scientific research and international collaboration in the space sector. The Duqm spaceport’s equatorial positioning is advantageous for rocket launches, taking advantage of the Earth’s rotational speeds.
National Space Policy and Executive Program: Oman unveiled a 10-year National Space Policy and Executive Program, spanning 2023-2033. This comprehensive strategy aims to establish a domestic industry supporting the assembly of satellites and space systems. The program is divided into three phases, focusing initially on space-related downstream activities, then moving to infrastructure development, and finally advancing into complex systems and capabilities.
Space Research Center: Plans are underway to establish a Space Settlement Center in the Duqm district’s Artificial Intelligence Zone. This center will enable the simulation of space environments for astronaut studies and other related research, significantly advancing Oman’s space research capabilities.
Space Sector Investment and Collaboration: Oman is actively working to attract investments in the space sector and participate in international collaborations. The country’s participation in global space economy meetings demonstrates its commitment to developing its space sector and achieving the objectives of Oman Vision 2040.
Qatar’s Space Sector Contributions
The Qatar Aeronautics and Space Agency (QASA) has been actively involved in space research and development. Qatar’s engagement in the space sector includes contributions to regional GCC projects and collaborations with other space agencies. These efforts are part of a broader movement in the GCC region to enhance capabilities in space technology and exploration.
Overall, the advancements in Oman and Qatar’s space sectors in 2023 are indicative of the growing importance of space exploration and technology in the GCC region. Both countries are investing in infrastructure, policy development, research, and international collaborations, paving the way for significant contributions to the global space industry.
Private Sector’s Role and Legal Challenges
The private sector is increasingly involved in space-related operations and services. Satellite services remain a mainstream revenue source for many space companies, with Euroconsult projecting satellite services revenue to reach $1.2 trillion by 2031. The sector has seen substantial mergers and acquisitions (M&A) activity, indicating a healthy and vibrant market.
However, this growth also brings legal and jurisdictional challenges, especially around liability, intellectual property, taxation, and dispute resolution. These legal complexities must be navigated as the sector continues to expand.
As 2023 draws to a close, the GCC’s space sector stands at a pivotal point. The region’s ambitious space endeavors, combined with strategic partnerships and private sector engagement, are shaping a new frontier in space exploration and technology. These developments not only enhance the GCC’s standing in the global space arena but also open up new opportunities for economic diversification, scientific advancement, and geopolitical influence.
At A Glance GCC Region's Space Sector Advancements in 2023 * Significant progress in space exploration and technology. * Growing role in the global space race due to technological advancements, strategic partnerships, and investments. Saudi Arabia * Transformation of the Saudi Space Commission into the Saudi Space Agency (SSA). * Launch of the first mission to the ISS, including the first female Arab astronaut. * Focus areas: tourism, photography, satellite communications, exploration. * Part of Saudi Vision 2030 for economic diversification and technological advancement. United Arab Emirates * Continued leadership in Arab world's space exploration. * Notable achievements: Emirati astronaut's six-month ISS mission, lunar mission with Rashid rover, launch of MBZ-Sat. * Establishment of space economic zones in Masdar City, Dubai, and Sharjah. * Emirates Mars Mission's impact on public interest and private space sector development. Bahrain * Launch of the first fully Bahraini-built satellite. * Collaboration with regional and international partners, including the UK. * Focus on sustainable development through space technologies. Kuwait * Private sector-led space initiatives. * Launch of "Kuwait Sat-1" by Kuwait University and funded by the Kuwait Foundation. * Emphasis on developing national expertise in space technology. Oman * Plans for the Middle East’s first space rocket launch center in Duqm. * 10-year National Space Policy and Executive Program. * Establishment of a Space Settlement Center in Duqm. Qatar * Active involvement in space research and development. * Contributions to regional GCC projects and collaborations with other space agencies. Private Sector's Role and Legal Challenges * Increasing involvement in space operations and services. * Legal and jurisdictional challenges in the growing space sector. Overall GCC Space Sector Outlook * Pivotal point in space exploration and technology. * Opportunities for economic diversification, scientific advancement, and geopolitical influence.