Riyadh, Saudi Arabia — The United States slashing foreign aid risks piling pressure on already acute humanitarian crises across the globe, a World Health Organization official said Sunday, also warning against withdrawing from the UN agency.
Since taking office in January, President Donald Trump has effectively frozen foreign aid funding, moved to dismantle the US Agency for International Development (USAID) and other programs, and announced plans to leave the WHO.
Washington, which had long been the WHO’s biggest donor, did not pay its 2024 dues, and it remains unclear if the United States will meet its membership obligations for 2025
The agency, already facing a gaping deficit this year, has proposed shrinking its budget by a fifth, likely reducing its reach and workforce, according to an earlier AFP report citing an internal email.
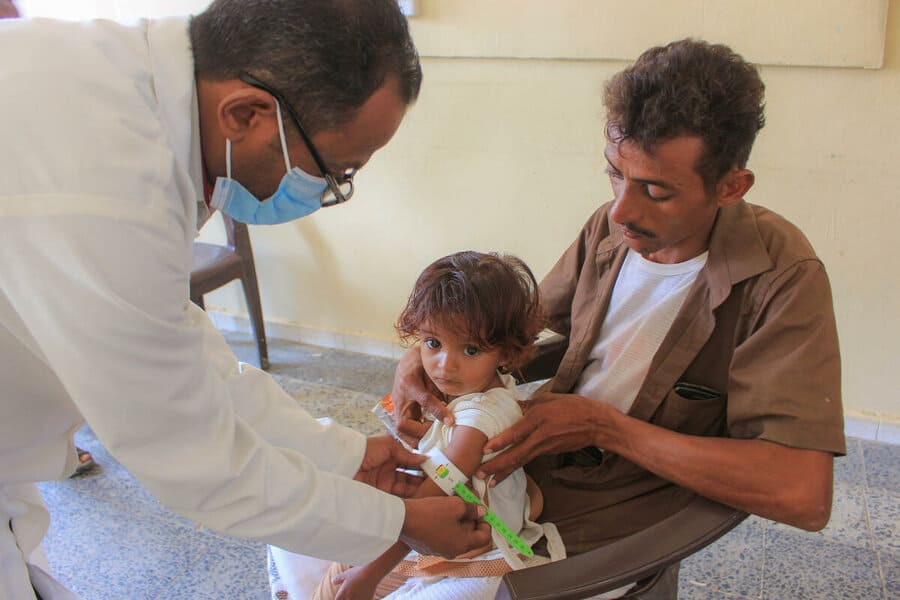
“The WHO with its partners have a significant role in sustaining healthcare systems, rehabilitation of healthcare systems, emergency medical team training and dispatching, pre-placement of trauma kits,” Hanan Balkhy, the WHO’s regional director for the Eastern Mediterranean, told AFP.
“Many of these programs have now stopped or are not going to be able to continue,” she said.
The funding cuts will likely hinder the ability to continue delivering robust aid to communities in desperate need of care.
Balkhy cited the ongoing conflicts in Gaza, Sudan, and Yemen as areas where healthcare institutions and aid programs were already under pressure before the funding shakeups.
In the Gaza Strip, where more than a year and a half of fighting has seen large swaths of the Palestinian territory reduced to rubble and few hospitals remain functioning, the public health situation is dire.
“The emergency medical team support, procurement of the medications and the rehabilitation of the health care facilities, all of that has been immediately impacted by the freeze of the US support,” said Balkhy.
In Sudan, the WHO is facing mounting issues amid a bloody civil war that has displaced millions, with several areas hit by at least three different disease outbreaks — malaria, dengue and cholera, according to Balkhy.
“We work significantly to identify emerging and re-emerging pathogens to keep the Sudanese safe, but also to keep the rest of the world safe. So it will impact our ability to continue to do surveillance, detection of diseases,” she added.
A US departure from the WHO will also undercut long established channels of communication with leading research facilities, universities and public health institutions that are based in the United States.
That in turn would likely prevent the easy sharing of information and research, which is pivotal to heading off global public health crises like an emerging pandemic, said Balkhy.
“These bacteria and viruses, number one, know no borders. Number two, they are ambivalent to what’s happening in the human political landscape.”